Insulin Signaling and Inflammation in Prostate Cancer: A Modern Perspective
The relationship between what we eat and prostate cancer is full of tricky parts and tangled issues that continue to challenge both clinicians and patients. Recent insights suggest that dietary factors, particularly those that affect insulin signaling and inflammation, play a key role in not only the risk of developing prostate cancer but also in disease progression. As prostate cancer increasingly takes on the characteristics of a chronic condition, it is essential to reframe our approach to dietary guidance as a critical part of survivorship care.
In the modern landscape of cancer care, we often find ourselves faced with a series of confusing bits when trying to piece together optimal diet strategies. This is especially true when we consider how both insulin and inflammation interact in the body. While review studies have pointed out that diets which spike insulin and trigger inflammatory responses are associated with a higher risk of prostate cancer, diets that work to lower these levels appear to be protective. This opinion editorial will take a closer look at these dietary pathways, offering insights into the practical application of new research findings and how patients can work through these issues with their care teams.
Understanding the Role of Insulin in Prostate Cancer
How High Insulin Levels Contribute to Cancer Growth
Insulin signaling is a crucial biological pathway that affects many parts of the body. When a person consumes high amounts of simple sugars and refined carbohydrates, it can lead to spikes in insulin. This is not only a concern for metabolic health but may also create a hormone-rich environment that can favor cancer cell growth. Studies have consistently shown that diets that produce high insulin responses are associated with increased risks of developing prostate cancer or experiencing its progression.
It is important to emphasize that this relationship is not strictly linear. Many factors contribute to insulin resistance, and the body’s response to different food types is affected by genetic predispositions and other lifestyle factors. However, the collective evidence suggests that managing insulin levels through targeted dietary choices is an essential piece of the puzzle.
Insulin Regulation: Digging Into the Biochemical Mechanisms
When we take a closer look at insulin signaling, we discover many little twists that illustrate just how intricate this process truly is. Insulin binds to specific cellular receptors, initiating a cascade of events that promote cell growth and proliferation. In benign circumstances, this is a necessary process. However, in a setting where cells begin to transform into malignant counterparts, high insulin levels may inadvertently fuel the growth of cancer cells.
For example, insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGF) often create an environment that supports rapid cell division. This means that any dietary pattern contributing to sustained high insulin levels could potentially make the cellular environment more prone to the development of prostate malignancies. As we figure a path through this evidence, it becomes clear that reducing the intake of simple sugars and other high-insulin-triggering foods is a practical step toward diminishing the risk.
Dietary Strategies for Lowering Insulin and Inflammation
Foods to Avoid: Tackling the Processed Pitfalls
The first step in formulating an effective dietary strategy for prostate cancer care is to understand the sources of risk. Ultra-processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and simple sugars are common culprits that prompt rapid spikes in blood glucose and subsequent insulin surges. By steering clear of these items, patients can significantly reduce one of the mechanisms that may promote cancer growth.
Here are some key points to consider when planning your diet:
- Avoid sugary drinks and snacks that provide a quick, yet fleeting, energy boost.
- Limit consumption of white bread, pastries, and other refined-carbohydrate-rich items.
- Be cautious of many pre-packaged meals that can be loaded with hidden sugars and additives.
These measures not only help in controlling insulin levels but also contribute to overall calorie regulation and weight management.
Adopting a Plant-Based, Whole Foods Diet
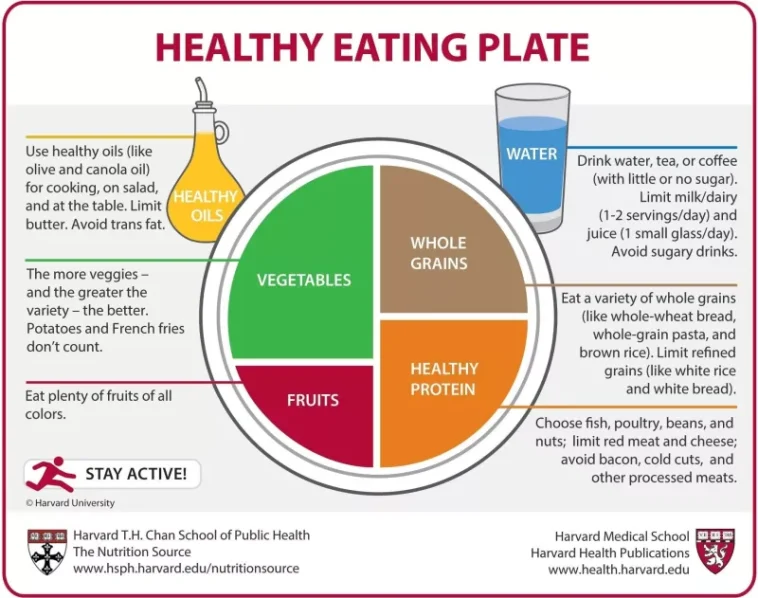
In contrast to the pitfalls of processed foods, plant-based diets that emphasize whole foods have been shown to lower insulin and inflammatory markers. Whether one follows a Mediterranean, low-carb, or strictly vegan diet, the underlying principle remains the same: choose foods that minimize processed components and maximize nutrient density.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats offers several benefits. Not only do these foods help control insulin levels, but they also provide antioxidants and other compounds that may help reduce inflammation. This dual effect makes plant-based diets a promising strategy in the context of prostate cancer care.
Comparing Low-Carbohydrate Approaches
Another approach that has garnered attention is the low-carbohydrate diet. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, particularly refined carbs, the body is forced to use fat as its primary energy source. This metabolic shift can lead to a more stable insulin response and reduced inflammation over time.
Low-carb diets have a number of proponents in the medical community, especially when it comes to managing metabolic conditions that may exacerbate prostate cancer. However, it is essential to tailor the approach to individual needs and ensure that any drastic changes are made under professional supervision.
Prostate Cancer as a Chronic Disease: Dual Benefits of Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
The Changing Face of Prostate Cancer Survivorship
With advances in systemic therapies, breakthroughs in imaging, and improved local interventions, prostate cancer today often resembles a chronic disease. In many cases, men can live for years with the condition. However, this longevity also brings to light the importance of managing other health risks that come with aging. In fact, heart disease has now emerged as the leading cause of death among prostate cancer survivors.
This shift calls for an integrated approach to care—one that considers both cancer prevention and cardiovascular health. Lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation do not just support prostate health; they also significantly lower the risks associated with heart disease.
Finding Your Path Through Combined Interventions
Integrating dietary changes with other lifestyle modifications offers a “twofer,” as some experts put it. By focusing on natural, unprocessed foods and avoiding harmful dietary triggers, patients may not only reduce their cancer risk but also experience improved cardiovascular outcomes. This holistic approach to health management means that patients get double the benefit from the adjustments they make in their day-to-day lives, with minimal risks and significant potential gains.
Below is a simple table that summarizes some of the key lifestyle modifications that can support both prostate and heart health:
| Intervention | Benefits for Prostate Health | Benefits for Cardiovascular Health |
|---|---|---|
| Whole-food, plant-based diet | Reduces insulin spikes and inflammation | Improves cholesterol levels and blood pressure |
| Low-carbohydrate approach | Stabilizes blood sugar levels | Promotes weight loss and insulin sensitivity |
| Regular physical activity | Enhances overall body function and metabolism | Improves heart function and circulation |
| Smoking cessation | Reduces cancer risk factors | Drastically improves cardiovascular health |
Real-World Application: From the Clinic to the Kitchen
Practical Advice for Clinicians Counseling Patients
For clinicians, discussing dietary changes during a short appointment can be nerve-racking, given the little details and subtle parts that must be considered. The challenge lies in distilling a massive amount of evidence into actionable advice that patients can follow once they leave the consulting room.
Dr. Stephen J. Freedland, a respected authority in urology, recommends a straightforward and practical approach to dietary counseling. Given the many twists and turns in current dietary studies, his guidance focuses on simplicity: advise patients to avoid simple sugars, ultra-processed foods, and refined carbohydrates. These are the usual suspects that contribute to rapid insulin spikes and inflammatory pathways.
An effective way to structure this conversation might include a quick checklist that patients can refer to:
- Steer clear of sodas, candies, and baked goods made from white flour.
- Emphasize whole-grain alternatives where possible.
- Encourage a shift toward natural, unrefined ingredients.
By keeping recommendations straightforward, clinicians can ensure that patients are not overwhelmed by the intimidating breadth of dietary advice available. Simplicity is key when encouraging long-term adherence, especially when patients are already managing a chronic condition.
Tools to Assist Patients in Making Better Choices
Modern technology and educational tools can help bridge the gap between complex nutritional science and everyday meal planning. Mobile apps, online nutrition guides, and even structured meal planning programs are available to help patients figure a path toward dietary success. Patients benefit from resources that break down the science into easy-to-understand visuals and actionable steps.
Healthcare providers might also consider offering or recommending dietary workshops where patients learn to cook simple, healthy meals at home. This hands-on experience can serve as a crucial step in working through the often intimidating process of overhauling one’s diet.
Tailoring Dietary Approaches: The Debate Between Mediterranean, Plant-Based, and Low-Carb Diets
Examining the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet has long been celebrated for its heart-friendly benefits and its emphasis on whole, natural foods. Rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil, this diet minimizes processed ingredients while providing a balanced supply of nutrients that help in managing insulin and inflammatory responses.
What makes the Mediterranean diet particularly appealing for prostate cancer management is its flexibility. Patients can enjoy a variety of foods, which makes long-term adherence more achievable. Furthermore, clinical observations have noted reductions in the markers of inflammation and improvements in insulin sensitivity among individuals following this diet.
Plant-Based Diets Take Center Stage
Plant-based diets, which stress the consumption of minimally processed fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, are also emerging as a super important strategy for those looking to reduce cancer risks. Beyond just controlling weight, these diets are loaded with antioxidants and compounds that help counteract the inflammatory processes known to be involved in cancer progression.
Furthermore, plant-based diets often naturally restrict the intake of dietary fats known to exacerbate insulin resistance. When patients replace animal proteins with plant proteins, they may experience additional benefits such as improved gut health and better overall metabolic function.
Low-Carb Diets: A Closer Look at Their Potential Benefits
Low-carbohydrate diets offer a different approach by specifically targeting the body’s reliance on carbohydrates for energy. By reducing the intake of refined carbohydrates, these diets help stabilize blood sugar levels and lead to a more predictable insulin response. For patients at risk of or dealing with prostate cancer, this can mean a reduction in one of the key players in the disease’s progression.
It is important to note, however, that low-carb diets are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Patients must consider personal preferences, metabolic needs, and any other underlying conditions before making a switch. Consultation with a nutritionist or healthcare provider is essential to craft a diet that works specifically for the individual.
Integrating Physical Activity and Other Lifestyle Changes
Beyond Diet: The Role of Exercise in Prostate Cancer Care
While dietary modifications are central to managing insulin levels and inflammation, physical exercise plays an equally important role in overall health. Although not the primary focus of recent dietary studies, vigorous physical activity is a super important component in supporting cardiovascular health and enhancing metabolism.
Regular exercise contributes to weight management and, importantly, helps maintain muscle mass and function. For prostate cancer survivors, this dual focus on diet and exercise means that even modest improvements in fitness can have far-reaching benefits, from reducing cancer risk to improving quality of life.
Here is how integrating physical activity complements dietary strategies:
- Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, mitigating the effects of sporadic high insulin levels.
- Regular physical activity helps regulate inflammation across the body.
- Physical exercise improves cardiovascular function, which is critical given that heart disease is a leading cause of death among prostate cancer survivors.
Simple Tips for Incorporating Active Lifestyles
For patients, here are a few easy-to-implement ideas to get started on an active lifestyle:
- Consider routine walks or light jogs as a way to get moving daily.
- Incorporate strength training exercises a few times a week to build muscle mass.
- Join a community exercise class or a local sports club for added motivation and social support.
By taking these small steps, patients can better manage their overall health, thus reducing the cumulative effects of both cancer treatments and everyday stressors.
Challenges in Translating Science Into Everyday Practice
Overcoming the Intimidating Task of Dietary Change
One of the most nerve-racking aspects of managing prostate cancer through diet is finding your way through the myriad of confusing bits and complicated pieces of nutritional advice. Healthcare providers often struggle with the challenge of transforming extensive and sometimes conflicting research data into practical, everyday actions that patients can apply.
The process is not only full of problems but is also laden with the tension of trying to get every fine point right. It is one thing to understand the science behind insulin and inflammation; it is another entirely to communicate this knowledge in a way that patients can integrate into their busy lives.
Clinicians are encouraged to adopt a straightforward approach: focus on the essentials and offer clear, concise recommendations rather than overwhelming patients with every subtle detail of dietary science. By doing so, they ensure that patients are armed with information that is both accessible and actionable.
Educational Resources and Community Support
To ease the transition, many experts advocate for more community-based education programs that cover not only dietary guidelines but also practical cooking skills. These community workshops help demystify the seemingly daunting task of rethinking one’s diet, breaking down the process into manageable, digestible steps.
Moreover, online forums, mobile apps, and nutritional guides can serve as powerful tools for patients and their families. The integration of technology in patient education often leads to improved adherence to recommended dietary patterns, as individuals can track their progress and occasionally receive feedback from healthcare professionals.
Future Directions: Research and Clinical Trials
Emerging Therapies and Their Dietary Implications
The evolving nature of prostate cancer treatment means that dietary recommendations may, in the future, be tailored even more closely to individual genetic and metabolic profiles. Advances in genomic testing and next-generation imaging have opened up new avenues for understanding how diet interacts with patient-specific risk factors.
Future clinical trials are expected to provide clearer guidance on how variations in diet may affect the efficacy of emerging systemic therapies. This development holds particular promise for patients who need personalized care that takes into account the hidden complexities of their unique biological makeup.
As research continues to build, the relationship between dietary patterns, insulin signaling, and inflammation will likely be refined. This journey will require close cooperation between nutritionists, oncologists, and researchers to work through the many little twists and turns presented by ongoing studies.
Personalized Nutrition: The Next Frontier
There is growing interest in the field of personalized nutrition, which involves tailoring dietary advice based on genetic markers, metabolic profiles, and even gut microbiome composition. With prostate cancer, this approach could allow for more nuanced strategies that address both the insulin-dependent mechanisms of cancer growth and the inflammatory tide that seems to drive disease progression.
By integrating personalized nutrition into clinical practice, healthcare providers may one day offer dietary interventions that are finely tuned to the individual, potentially transforming the way we approach prostate cancer care. Such a shift could ultimately lead to more effective suppression of the disease while also improving overall quality of life.
Weaving It All Together: A Balanced Approach to Health
The Interplay of Diet, Exercise, and Survivorship Care
In today’s healthcare environment, the management of prostate cancer is moving toward a more holistic view that encompasses dietary interventions, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications. The evidence points to a clear message: simple sugars, ultra-processed foods, and refined carbohydrates can be harmful, while whole foods, whether from plant-based or low-carb diets, hold promise as protective dietary strategies.
This dual approach not only has the potential to reduce the risk of prostate cancer progression but also enhances cardiovascular health—a benefit that is especially important given the chronic nature of the disease in many men. With heart disease being a leading cause of death among this population, the integration of diet and exercise in survivorship care is super important.
Below is a bullet list summarizing the key lifestyle modifications that can create a healthier overall picture for prostate cancer survivors:
- Avoid high-glycemic index foods that lead to rapid insulin surges.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to reduce inflammation.
- Adopt a consistent dietary pattern, whether Mediterranean, plant-based, or low-carb.
- Engage in regular physical activity to boost metabolism and heart health.
- Take advantage of community and digital resources for support and education.
Clinical Reflections on Dietary Counseling
As clinicians continue to work through the challenges of conveying these complex topics during brief appointments, it is critical to remember that dietary changes need not be overwhelming. By breaking down the confusing bits into practical, easy-to-follow steps, healthcare providers can empower their patients to make lasting changes.
This opinion editorial is not meant to prescribe a one-size-fits-all solution but rather to emphasize the importance of integrating dietary strategies into comprehensive prostate cancer care. With steady advances in both research and clinical practice, we are beginning to see the benefits of a balanced approach that acknowledges the intertwined roles of diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle in shaping health outcomes.
Concluding Thoughts on Dietary Pathways and Prostate Cancer
A Call for Holistic and Individualized Patient Care
In wrapping up this discussion, it is clear that the journey toward better prostate cancer outcomes is as much about managing insulin and inflammation as it is about embracing a comprehensive, healthy lifestyle. The evidence is robust: dietary patterns play a pivotal role in modulating the biological environment that predisposes men to prostate cancer progression, all while influencing their cardiovascular health in significant ways.
Clinicians and patients alike must work together to find practical and sustainable methods to incorporate dietary changes into daily routines. Though the task may seem intimidating at first, simplicity and consistency are the keys to long-term success. By focusing on the reduction of refined sugars and processed foods and by embracing whole foods, patients can take concrete steps toward better health.
It is also important for the medical community to continue supporting research that refines our understanding of these mechanisms. More detailed studies and future clinical trials will help tease apart the subtle details underlying the interplay between diet, insulin, and inflammation.
Looking Forward: Merging Research With Everyday Practice
Looking toward the future, the integration of personalized nutrition, the aid of digital health tools, and continual community-based support will be critical in making sure that dietary recommendations are not just theoretical but accessible and practical. The healthcare community is on the brink of a new era where every patient can receive tailored advice that considers both the big picture and the little twists of their personal health journey.
In summary, the current body of evidence places dietary choices at the forefront of prostate cancer management. By reducing foods that contribute to high insulin spikes and inflammation, patients can not only slow the progression of prostate cancer but also diminish their risk of cardiovascular disease. As research continues to evolve, embracing a balanced, holistic lifestyle will remain a cornerstone of effective cancer care.
Ultimately, the power to steer through this complex health landscape lies with informed choices and continual collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. By adopting a balanced approach that fuses straightforward dietary guidelines with the supportive structures of modern technology and community engagement, we can help ensure that prostate cancer care is both effective and sustainable over the long haul.
Final Reflections
The dietary pathways in prostate cancer are undeniably linked to the biological processes governed by insulin and inflammation. As we take a closer look at how everyday foods influence these mechanisms, it becomes evident that proactive dietary strategies are a super important part of the overall care framework. Whether it is through avoiding processed sugars, embracing plant-based meals, or integrating low-carb approaches, each patient can find a method that best fits their unique needs and lifestyle.
While the challenges associated with making these dietary transitions may be intimidating, the cumulative benefits—in terms of both cancer control and heart health—are too significant to ignore. In the continuous effort to empower patients, it is crucial that the medical community remains committed to providing clear, concise, and actionable dietary advice that cuts through the confusing bits and little twists of modern nutritional science.
For clinicians, caregivers, and patients alike, the journey is about more than just managing a diagnosis; it’s about actively taking part in a healthier future. With every healthy meal, every session of physical activity, and every informed decision, there is added potential to improve overall outcomes and quality of life. The road may be long and filled with tangled issues, but by working hand in hand, we can pave a path toward better health and a more hopeful future in prostate cancer care.
Originally Post From https://www.urologytimes.com/view/dietary-pathways-in-prostate-cancer-insulin-and-inflammation
Read more about this topic at
Inflammation and insulin resistance – PMC
7-Day Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan for Insulin Resistance